Home > Learn Python in 2025: an Essential Language
In 2025, learning Python has become an almost essential step for anyone wishing to grow in the field of technology and digital innovation. For several years, Python has established itself as one of the most widely used programming languages, thanks to its simplicity, versatility, and a constantly expanding ecosystem of tools. Whether it’s artificial intelligence, data science, web development, automation, or cloud computing, Python is everywhere.
Its success is based on a clear philosophy: a readable, intuitive language close to natural language. Unlike more complex languages such as C++ or Java, Python enables developers to achieve results quickly, making it an ideal entry point for beginners. At the same time, its power and the richness of its libraries make it a favorite tool among experienced professionals working on large-scale projects.
The demand for Python skills continues to grow in the job market. Companies are looking for professionals able to analyze massive data sets, design modern web applications, develop predictive models, or automate business processes. By choosing Python training, you are investing in a lasting, in-demand skill, relevant both to today’s careers and those of the future.

Python is now regarded as a universal language. Its clear syntax reduces comprehension time and limits errors, which encourages collaboration within development teams. It supports several programming paradigms (procedural, object-oriented, and functional), making it adaptable to various contexts. This flexibility explains why Python is used both to write small automation scripts and to design complex, distributed systems.
In 2025, Python remains resolutely modern. Its ecosystem evolves continuously: new libraries emerge every year, while existing tools keep improving. Web frameworks such as Django and Flask, machine learning solutions like TensorFlow or PyTorch, and data engineering tools such as Airflow and Dask all reinforce Python’s role as a reference language. Moreover, Python benefits from massive support from its global community: tutorials, forums, events, documentation… so many resources that make learning and mastering it easier.
Major companies like Google, Microsoft, Meta, and Netflix use this programming language daily for critical applications. This widespread adoption in the industry proves that Python is not a passing trend, but rather a lasting and strategic choice.

Python stands out for its unique versatility, making it a language suited to almost any context. With a rich ecosystem of several hundred thousand packages on PyPI, it can be extended to meet a wide variety of needs. This depth makes it indispensable in areas as diverse as data science, artificial intelligence, web development, cloud computing, and network automation. In 2025, these are the main sectors where Python plays a key role.
Python holds a central place in AI and machine learning. Frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch simplify the creation and training of complex deep learning models, used in image recognition, natural language processing, and behavior prediction. In 2024, these frameworks received major updates, further enhancing their efficiency. In 2025, almost every AI project naturally relies on Python as its main language.
Data science remains one of the flagship domains for this language. Pandas for data manipulation, NumPy for scientific computing, and Matplotlib/Seaborn for visualization provide a complete toolkit to turn raw data into actionable insights. On the machine learning side, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, as well as XGBoost and LightGBM cover the majority of use cases, from classic models to deep neural networks.
Python also excels in web development. Django 5.0 structures robust, “batteries-included” applications, Flask 3.0 favors lightness and modularity, and FastAPI (0.x branch) stands out for its asynchronous APIs and automatic documentation. Together, these frameworks enable the design of websites and robust, secure, and scalable applications.
In 2025, Python holds a prime position in cloud computing. Thanks to its integrations with AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions, it’s used to build serverless functions, deploy scalable applications, and automate pipelines. On the SDK side, Boto3 (AWS), google-cloud-python (GCP), and azure-sdk-for-python (Azure) are de facto standards. For Infrastructure as Code, Python is used with Terraform (via modules and scripts) and Pulumi to model and provision infrastructure.
Automation is one of Python’s most widespread uses. In networking, Netmiko, NAPALM, and Ansible modules automate the configuration of multi-vendor devices and infrastructures. On the security side, Scapy, Impacket, and Mitmproxy provide tooling for traffic analysis, auditing, and penetration testing. Vendors such as Cisco, Juniper, Fortinet, and Check Point expose Python SDKs/APIs, enabling organizations to gain efficiency and improve reliability.

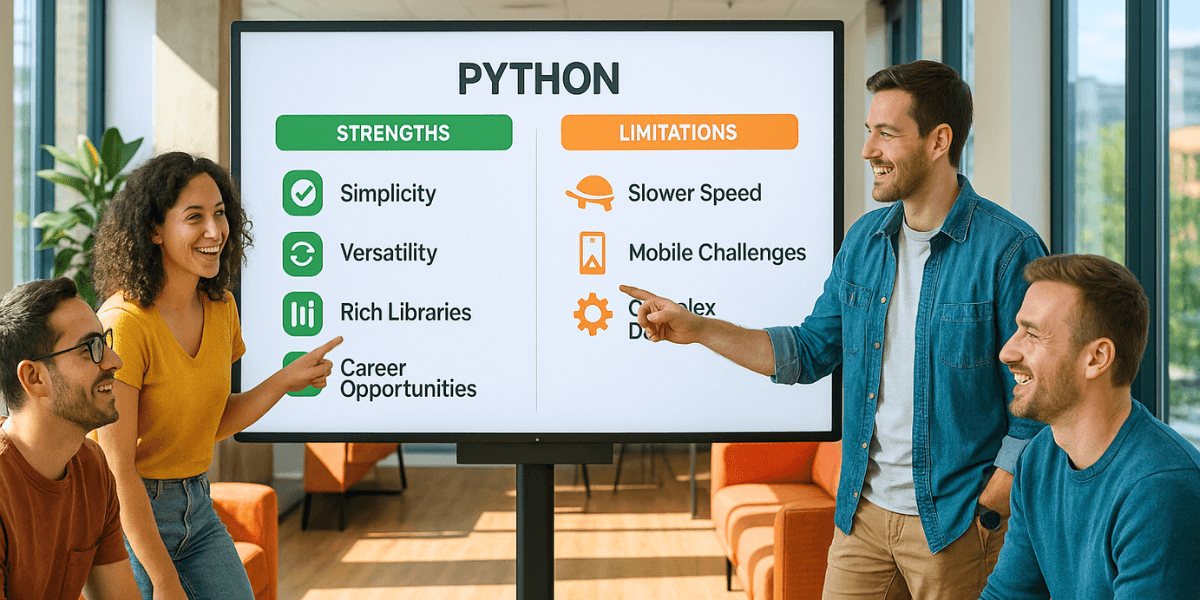
If Python is so successful, it is primarily thanks to its many strengths. Its simple syntax allows beginners to progress quickly and experts to save time when writing code. Library ecosystem covers virtually every need: data analysis, artificial intelligence, web development, automation, visualization, and more. Its large and active community is a valuable resource for learning, solving problems, and staying up to date. Finally, Python is one of the most in-demand languages on the job market, making it a strategic asset for any career.
However, it also has certain limitations. Its execution speed is lower than compiled languages like C++ or Rust for very intensive workloads. To mitigate this constraint, you can target hot spots with Numba, Cython, PyPy, or C/C++ extensions. Mobile development isn’t its primary use, but alternatives like Kivy or BeeWare exist. Finally, dependency management can become complex on large projects, hence the value of tooling and good packaging practices.
In 2025, there are many ways to learn Python depending on your needs and pace. Online courses provide great flexibility, intensive bootcamps allow for rapid skill-building, while in-person training favors direct interaction with instructors and other learners. Each approach has its benefits, but all rely on a common principle: consistency. Dedicating a little time every day to practice is far more effective than long, irregular sessions.
Before you start, it is essential to define a clear goal. Do you want to use Python for data science, web development, artificial intelligence, or process automation? Your choice will guide which libraries and frameworks to focus on, whether it’s Pandas, Django, TensorFlow, or IT orchestration tools.
Choosing a Python training course with ITTA means benefiting from the guidance of recognized experts. The programs are adapted to different levels: beginner courses for newcomers, advanced training for experienced developers, or specialization in data science, artificial intelligence, and web development. The courses combine theory and practice, with real-world case studies that allow immediate application of the concepts studied. Thanks to a flexible format, available both in-person and online, ITTA enables everyone to learn Python at their own pace with a Python course. In 2025, training with ITTA means acquiring skills directly applicable in business and valued on the job market.
Python certifications are an excellent way to validate your skills. Among the most recognized are PCEP (Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer) and PCAP (Certified Associate in Python Programming). For more advanced profiles, some cloud certifications, such as those offered by Microsoft Azure, include Python as part of their learning paths.

In 2025, mastering Python isn’t just about writing code—it’s a strategic skill that opens doors to a wide range of fast-growing careers. In data science, companies look for profiles able to leverage Pandas, NumPy, or Scikit-learn to turn massive data volumes into strategic insights. Data analysts use Python to automate reporting, while data scientists build predictive models integrated into decision-making processes.
In web development, Python remains a safe bet thanks to Django, Flask, and FastAPI. Developers who master these frameworks design robust and secure platforms capable of supporting millions of users. The growing demand for modern APIs to interconnect services and applications also multiplies opportunities in this field.
Machine learning engineers and AI specialists leverage TensorFlow or PyTorch to build solutions for image recognition, natural language processing, or anomaly detection. With the rise of generative AI, these profiles are particularly in demand.
In cloud computing and DevOps, Python serves as a key language for automating infrastructure deployment, orchestrating CI/CD pipelines, and managing serverless environments. Engineers who combine Python with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud are among the most sought-after in the market. Finally, cybersecurity increasingly relies on Python to develop penetration testing tools, log analysis solutions, and threat detection systems.
To stand out, it is advisable to pair Python with a business specialization: Python and data science, Python and cloud, Python and cybersecurity, or Python and web development. Coupled with an appropriate Python training, this approach transforms technical expertise into a real career accelerator, with sustainable opportunities in constantly innovating sectors.

In 2025, Python establishes itself as the universal language of modern technology. Simple, powerful, and extensible, it adapts both to the needs of beginners and to the most complex projects. Present in data science, artificial intelligence, web development, cloud, and automation, it remains a major asset for building a solid career. Taking a Python training course is an investment in a highly sought-after, versatile, and future-oriented skill. More than just a language, Python has become a true passport to success in the digital world.
Why learn Python in 2025?
Because it remains one of the most in-demand and versatile languages. It leads in data science, AI, web development, cloud, and automation, with a rich ecosystem of several hundred thousand packages on PyPI.
Is Python suitable for beginners?
Yes. Its simple, readable syntax helps you progress quickly, write clear code, and focus on problem-solving rather than language complexity.
What jobs can you do with Python?
Many roles: data analyst, data scientist, web developer (Django, Flask, FastAPI 0.x), machine learning engineer, cloud/DevOps engineer, network & security specialist.
What are Python’s limits and how to mitigate them?
Python is slower than C++/Rust for intensive workloads. You can optimize hotspots with Numba, Cython, PyPy, or C/C++ extensions. Dependency management can get complex—use isolated environments (venv/conda), a package manager (pip/poetry), and lockfiles.
Is Python useful for mobile?
It’s not its primary use, but options exist: Kivy and BeeWare let you build cross-platform mobile apps. For fully native needs, prefer iOS/Android stacks.
How does Python fit into cloud and DevOps?
Python integrates natively with AWS Lambda (Boto3), Google Cloud Functions (google-cloud-python), and Azure Functions (azure-sdk-for-python). It’s used with Terraform (modules, scripts) and Pulumi for Infrastructure-as-Code, and across CI/CD pipelines (testing, linting, packaging).
Which Python training should I choose in 2025?
Depends on your goals: for data, focus on Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn; for web, Django 5.0, Flask 3.0, FastAPI 0.x; for AI/ML, TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, LightGBM; for cloud/DevOps, cloud SDKs and IaC. A structured course (e.g., ITTA) accelerates learning and real-world application.

ITTA is the leader in IT training and project management solutions and services in French-speaking Switzerland.
Our latest posts
Subscribe to the newsletter
Consult our confirmed trainings and sessions

Nous utilisons des cookies afin de vous garantir une expérience de navigation fluide, agréable et entièrement sécurisée sur notre site. Ces cookies nous permettent d’analyser et d’améliorer nos services en continu, afin de mieux répondre à vos attentes.
Monday to Friday
8:30 AM to 6:00 PM
Tel. 058 307 73 00
ITTA
Route des jeunes 35
1227 Carouge, Suisse
Monday to Friday, from 8:30 am to 06:00 pm.