Home > OneDrive for Business: 10 Rules to Properly Secure and Organize Your Files
With the rise of remote work and ongoing digital transformation, OneDrive has become a go-to tool for storing and sharing business files. However, widespread adoption also comes with risks: in Switzerland, cyber threats continue to put pressure on companies, as highlighted by the “SME Cybersecurity 2025” study shared via the Confederation’s SME portal (kmu.admin.ch). At the same time, data breaches cost an average of $4.88 million (IBM). In Switzerland, under the revised Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP), fines (up to CHF 250,000) generally target responsible individuals and apply to certain intentional violations (EDÖB). So, how do you use OneDrive for Business securely? What best practices help protect sensitive data? This guide shares 10 essential rules to turn OneDrive into a safe, well-organized, high-performing workspace.

Businesses now store massive volumes of data in the cloud. OneDrive for Business provides 1 TB per user by default, and it is typically expandable up to 5 TB depending on the plan. Beyond that, increases up to 25 TB can be configured for specific needs (subject to conditions/eligibility) (Microsoft Learn ; Microsoft Learn). This capacity makes it possible to centralize documents, contracts, client files, and strategic data.
However, centralizing information also creates a prime target for cybercriminals. In 2024, 73% of data breaches stem from phishing and stolen credentials (NinjaOne). In addition, human error accounts for around 90% of cybersecurity incidents according to multiple studies. That’s why proper configuration is essential to protect OneDrive effectively.
Companies based in Switzerland must also meet strict data confidentiality requirements. Since September 2023, the revised Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP) provides for sanctions in the case of intentional violations and generally targets responsible individuals (EDÖB). Even though OneDrive benefits from certifications and fits within a security-focused approach, administrators still need to enable several protective features manually. Without these settings, files remain exposed to accidental sharing, unauthorized access, and data leaks.

Two-factor authentication is the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Even if an attacker gets the password, they won’t be able to access the account without the second factor. This measure dramatically reduces the risk of compromise.
To enable MFA for OneDrive for Business, several options are available. First, download Microsoft Authenticator on your smartphone. Then, go to your Microsoft 365 account security settings. Select “Two-step verification” and follow the instructions.
Several verification methods are supported: an authenticator app (recommended), SMS, phone call, or physical FIDO2 security keys. The Authenticator app provides the best balance between security and convenience. SMS is less secure because it can be intercepted. Finally, always store your recovery codes somewhere safe.

OneDrive uses AES 256-bit encryption to protect data at rest, while TLS 1.2 secures data in transit (Microsoft Learn). Each file is encrypted with a unique key, and those keys are stored separately from the data. This architecture ensures that no single component can provide access to your files on its own.
For sensitive documents, rely on features that truly fit a work/school environment: sensitivity labels (Microsoft Purview) with encryption and restrictions, DLP to reduce risky sharing, and Conditional Access to enforce rules based on device, location, or risk level. These mechanisms strengthen confidentiality without relying on options that are reserved for personal accounts.
Some organizations also add client-side encryption (files are encrypted before they are uploaded to the cloud). In that case, avoid depending on discontinued services: Boxcryptor has been discontinued (boxcryptor.com). If this is a real need, it must be properly scoped (support, governance, key management, recovery procedures) and validated by IT/security.

Sharing mistakes are one of the leading causes of data leaks. OneDrive offers several link types, each with a different security level. Understanding these options helps prevent accidental exposure.
For every share, define permissions precisely: view only, edit, or full control. Block downloads when needed to prevent files from being copied. Add an automatic expiration date and, if required, protect the link with a password. These measures greatly reduce the risk of uncontrolled distribution.
In a business environment, sharing security shouldn’t rely only on user best practices. At the admin level, limit or disable “Anyone” links across the tenant, enforce automatic link expiration, and control external sharing through policies. These settings significantly reduce leak risk, even when human error happens.
Regularly review files that are shared externally. OneDrive lets you check sharing history and revoke access instantly. This is especially useful when an employee leaves the company or when an external partner’s engagement ends. Never leave permanent access in place without oversight.

A well-designed folder structure makes it easier to find files and reduces misfiling. Several approaches work: organizing by project, department, client, or year. The key is to choose a consistent system and stick to it.
Adopt a standardized naming convention for all files. For example: YYYYMMDD_Document-name_Version. This structure helps sort files chronologically and quickly identify their content. Avoid special characters such as /, \, “, ‘, <, >, :, *, ? as they can cause technical issues.
Keep folder depth to 3–4 levels to avoid unnecessary complexity. Use clear, descriptive names. Also remember that syncing is constrained by the operating system (Windows/macOS). In Windows Explorer, the practical path length limit is around 256 characters, which makes shallow folder structures important (Microsoft Support). Finally, train all employees on these conventions to ensure they are followed.

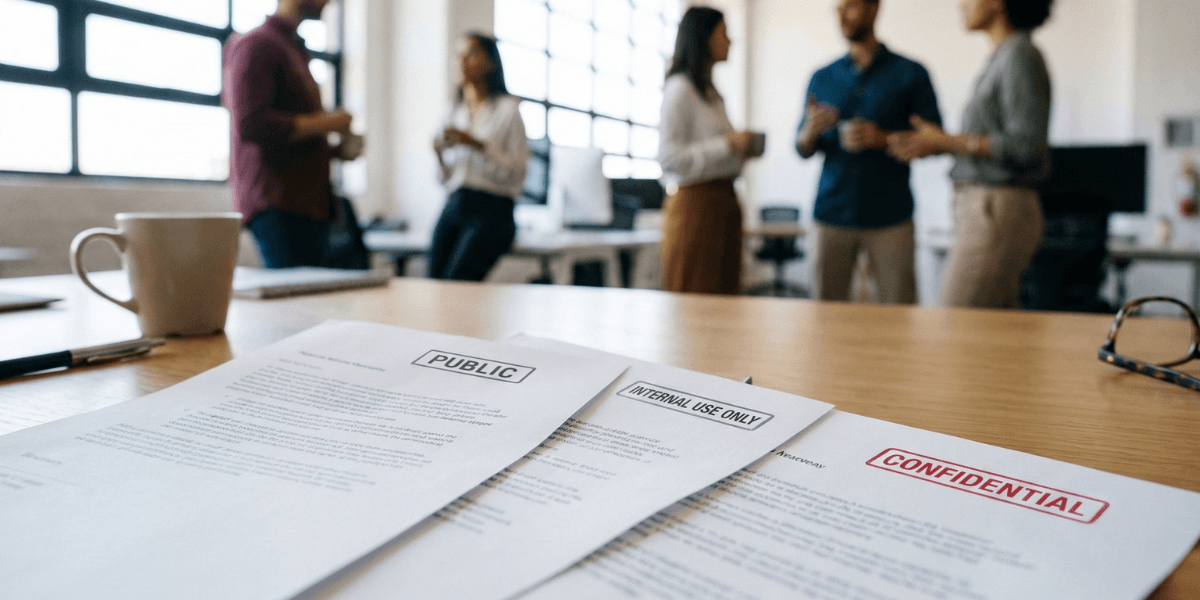
Microsoft Purview Information Protection can automatically classify documents based on sensitivity. Built into OneDrive for Business, it applies restrictions according to the confidentiality level. It’s a powerful tool for data governance.
Define classification levels that fit your organization. Typical examples include: Public (available to everyone), Internal (employees only), Confidential (restricted access), and Secret (maximum protection). Link each level to automatic controls: printing restrictions, external sharing blocks, stronger encryption, and more.
DLP (Data Loss Prevention) policies can automatically detect sensitive data such as credit card numbers, customer details, or personal information. When a user tries to share a document that contains these elements, the system can block the action and trigger an alert. This automation greatly reduces the risk of human error.

Each OneDrive for Business user has 1 TB of storage by default. Depending on the plan, this can typically be increased up to 5 TB, and beyond that, increases up to 25 TB may be available for specific needs (subject to conditions/eligibility) (Microsoft Learn ; Microsoft Learn). If a quota is reached, syncing can stop and data may be at risk. Proactive management is essential.
Use Files On-Demand to free up local disk space without deleting files from the cloud. This feature shows all files in File Explorer but only downloads them when you open them. It’s especially useful on laptops with limited storage.
Regularly identify large and outdated files. Archive old projects or move very large files to SharePoint or Teams. Keep in mind that the OneDrive recycle bin retains deleted files for 93 days. Empty it periodically to reclaim space. Finally, compress large files when it makes sense.

In a business environment, version history doesn’t have a fixed limit: it depends on the versioning policy defined by the organization (tenant/site/library) (Microsoft Support ; Microsoft Learn). This feature lets you roll back to an earlier version in case of accidental edits, corruption, or a ransomware attack. It’s a valuable safety net.
The Restore your OneDrive feature lets you roll back your entire OneDrive to a previous point in time after an attack. OneDrive can detect suspicious activity, such as mass file modifications. It then sends a notification and offers to restore the account to a specific date (Microsoft Support).
This protection is particularly useful against ransomware that encrypts files. In the event of malicious activity, OneDrive can restore your space to an earlier state (up to 30 days) and rely on version history based on your organization’s policy (Microsoft Support).

Technology alone isn’t enough. Employees are both the biggest vulnerability and the strongest line of defense. Regular training is essential to reduce human error, which is behind most security incidents.
Write a clear document that defines usage rules: naming conventions, sharing policy, handling of sensitive data, and incident procedures. All employees should acknowledge this policy during onboarding. It becomes a reference point if issues arise.
Run hands-on workshops on security features. Show how to enable MFA, apply sensitivity labels, and review sharing permissions. Practical demos are more effective than long manuals. You can also test awareness with phishing simulations to measure vigilance.

The Microsoft 365 admin center includes many settings to strengthen overall security. These controls apply across the organization and complement individual measures. Only admins can access them.
Configure DLP rules to automatically block the sharing of sensitive data. For example, prevent external sharing of documents containing Swiss AHV/AVS numbers, banking details, or medical information. The system analyzes content in real time and blocks non-compliant actions.
Enable audit logs to track all actions in OneDrive: access, edits, sharing, deletions. These logs help detect abnormal behavior quickly and provide essential evidence during an incident. Keep logs long enough to meet Swiss nFADP expectations, while remembering that penalties mainly target responsible individuals in cases of intentional violations (EDÖB).
OneDrive, SharePoint, and Teams form a coherent ecosystem. Each plays a specific role: OneDrive for personal files, SharePoint for team sites and collaborative projects, and Teams for conversations and channels. Understanding how they work together improves collaboration.
When you share a large file by email, Outlook can automatically insert a OneDrive link instead of attaching the file. This avoids the 25 MB attachment limit and ensures recipients always access the latest version. Permissions also remain controlled through OneDrive.
In Teams, files shared in private chats are stored in OneDrive, while files shared in channels are stored in SharePoint. This logical separation helps manage access. Still, consider backing up this data with a third-party solution to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies, two different media, one offsite).

Securing and organizing OneDrive for Business requires a holistic approach that combines technology, processes, and training. The 10 rules in this guide cover the essentials: stronger authentication, encryption, permission management, file organization, data classification, quotas, version history, user awareness, administrative policies, and Microsoft 365 integration.
By applying these recommendations, Swiss and international organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyberattacks and data leaks. In Switzerland, under the nFADP, fines (up to CHF 250,000) generally target responsible individuals and apply to certain intentional violations (EDÖB). But beyond the financial aspect, reputation and customer trust are on the line. OneDrive can then become a powerful, secure tool that supports collaboration while protecting your information assets.
Cybersecurity isn’t a destination, it’s an ongoing process of improvement and adaptation to new threats. Train your teams regularly, audit your configurations, and stay informed about how OneDrive for Business works and the latest protection features available.
How does OneDrive for Business work compared to the personal version?
OneDrive for Business provides 1 TB of storage by default, typically expandable up to 5 TB depending on the plan, with increases up to 25 TB available in specific cases (subject to conditions/eligibility) (Microsoft Learn ; Microsoft Learn). It includes advanced security features (DLP, classification labels, auditing) and is owned by the organization rather than the individual user. It also integrates natively with SharePoint and Teams for efficient business collaboration.
Are my OneDrive for Business files truly private?
OneDrive for Business files are legally owned by the organization. Administrators can access them when needed, including when an employee leaves. To strengthen confidentiality for sensitive documents, use sensitivity labels (Purview) with encryption and restrictions, DLP policies, and Conditional Access based on your security requirements.
Can I recover a file deleted more than 93 days ago?
By default, the OneDrive recycle bin retains deleted files for 93 days. After that, an admin may try recovery via the second-stage recycle bin, but it isn’t guaranteed. A third-party backup solution such as Veeam or AvePoint becomes essential if you need longer retention and stronger business continuity.
How can I prevent downloads of a shared file?
When sharing, open the advanced options and uncheck “Allow download.” This forces online viewing only and prevents users from saving a local copy. It can apply to both internal and external sharing and helps reduce unauthorized distribution.
Is OneDrive for Business compliant with the Swiss nFADP?
OneDrive can support an nFADP-compliant approach, but full compliance also depends on your configuration (labels, DLP, audit logs) and your internal processes for handling and reporting data breaches. Note that under the nFADP, criminal penalties (up to CHF 250,000) mainly target responsible individuals and apply to certain intentional violations (EDÖB).

ITTA is the leader in IT training and project management solutions and services in French-speaking Switzerland.
Our latest posts
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Consult our confirmed trainings and sessions

Nous utilisons des cookies afin de vous garantir une expérience de navigation fluide, agréable et entièrement sécurisée sur notre site. Ces cookies nous permettent d’analyser et d’améliorer nos services en continu, afin de mieux répondre à vos attentes.
Monday to Friday
8:30 AM to 6:00 PM
Tel. 058 307 73 00
ITTA
Route des jeunes 35
1227 Carouge, Suisse
Monday to Friday, from 8:30 am to 06:00 pm.