Home > Top 10 Best Databases to Use in 2024
Choosing the right database for 2024 is a strategic decision that can transform your business. But with a multitude of options available, how do you know which one will best meet your needs? Whether you are looking for high performance, flexibility, or robustness, certain databases stand out for their unique features and ability to handle massive volumes of information. MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, or MySQL: each solution has advantages and limitations that are crucial to understand in order to make the right choice. In this article, we reveal the top 10 databases not to miss in 2024. So, are you ready to discover which one will propel your business to new heights?

The best databases are the backbone of modern business growth. They provide quick access to critical information, allowing companies to make informed decisions and improve their overall performance. In 2024, the importance of databases continues to grow, as they have become indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes.
A database management software is essential for storing and managing an organization’s valuable data. Database management systems (DBMS) allow for easy addition, modification, and deletion of data, eliminating multiple entries and reducing errors. Moreover, using a database ensures data integrity and security while improving the overall system’s performance.
With the rise of Big Data, companies now have access to unprecedented amounts of data. This trend requires robust databases capable of processing and analyzing large volumes of information quickly and efficiently. Therefore, choosing the right database for your needs becomes a strategic priority for any organization looking to stay competitive in 2024.
MongoDB has established itself as a must-have among NoSQL databases in 2024. This open-source, document-oriented database offers great flexibility with its schema-less structure, allowing for variable data structures. MongoDB’s JSON documents allow multiple types of data to be grouped under a single entry, facilitating the organization and access to information.
In addition to its flexibility, MongoDB offers advanced features such as sharding and map-reduce functions, ensuring near-linear scalability when adding servers. These characteristics make MongoDB an ideal choice for applications requiring efficient management of large data volumes.
One of MongoDB’s main advantages lies in its flexibility. With its flexible schema, it’s possible to add new fields to documents at any time, making it easy to adapt the database to changing application needs. This flexibility is especially useful in environments where data structures evolve rapidly and require frequent adjustments.
Moreover, MongoDB has a powerful aggregation framework that allows for complex analyses and optimized searches through efficient indexing.
Finally, this database benefits from the support of an active community that contributes to its continuous development and growing adoption across various industries.
However, MongoDB is not without its drawbacks. One major challenge is its high memory consumption, which can become problematic when handling large volumes of data. In such scenarios, resource optimization is often necessary to ensure acceptable performance.
Furthermore, learning and mastering MongoDB may require specialized training due to its differences from traditional relational databases.

PostgreSQL is often praised for its reliability and robustness as an open-source relational database. As an object-relational database, PostgreSQL offers great flexibility and is compatible with most platforms, including Linux systems, virtual, physical, and cloud environments.
This adherence to standards makes PostgreSQL an ideal choice for transactional applications that require strict data integrity.
One of the key features of PostgreSQL is its support for the JSON format, allowing for efficient manipulation and querying of data in JSON format. This capability is enhanced by the hstore extension, which facilitates the storage of key-value pairs and provides a flexible alternative to JSON.
PostgreSQL also offers integrated development tools that simplify the management and deployment of databases, making it easier to administer complex systems.
PostgreSQL is adopted by many companies for its strong features and reliability. Here are some examples of companies using PostgreSQL:
These companies have integrated PostgreSQL into their critical data management strategies.
They benefit from PostgreSQL’s ability to efficiently manage large amounts of data, improving the performance of their systems and their capacity to make decisions based on reliable data.

Oracle Database is renowned for its high performance and solid market reputation for many years. This database offers advanced features such as AutoML, autonomous management, and support for multiple models, making it a preferred choice for many enterprises.
Additionally, Oracle Database is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, UNIX, Linux, and macOS, offering great deployment flexibility.
One of Oracle Database’s main strengths is its built-in security, which protects sensitive company information. This security is crucial for organizations dealing with sensitive data, ensuring that their information remains protected against unauthorized access.
Additionally, Oracle Database offers a wide range of useful tools for enterprise data management, making it easier to manage complex databases and improve operational efficiency.
However, the costs associated with Oracle Database are often considered high, which can be an issue for smaller businesses with limited budgets. Additionally, implementing Oracle Database can be complex, requiring specialized technical resources for proper configuration.
These factors may make Oracle Database less accessible for some organizations.

MySQL is one of the most popular open-source databases, widely used for web applications due to its high performance and reliability. The free version of MySQL offers sufficient speed and reliability for many applications, while the paid version is intended for organizations with specific needs.
One of the main advantages of MySQL is:
However, MySQL can experience performance issues with very large data sets. This performance issue is particularly relevant when databases exceed a certain size, requiring more complex memory management.

Microsoft SQL Server offers innovations in security, accessibility, and exploitation, making it a comprehensive solution for modern businesses. It provides strong transactional support and integration with other Microsoft services, making it easier to manage critical data.
Moreover, it is compatible with Windows and Linux operating systems, offering flexible options for cloud deployment.
Microsoft SQL Server stands out for its ease of use and integration with Azure, making it a powerful solution for advanced analytics. SQL Server’s OLTP engine allows for quick data access, further enhancing security and analytics efficiency.
Microsoft SQL Server offers advanced data analysis and reporting capabilities. This database is widely considered a critical solution for businesses requiring advanced data management, optimizing their critical operations.

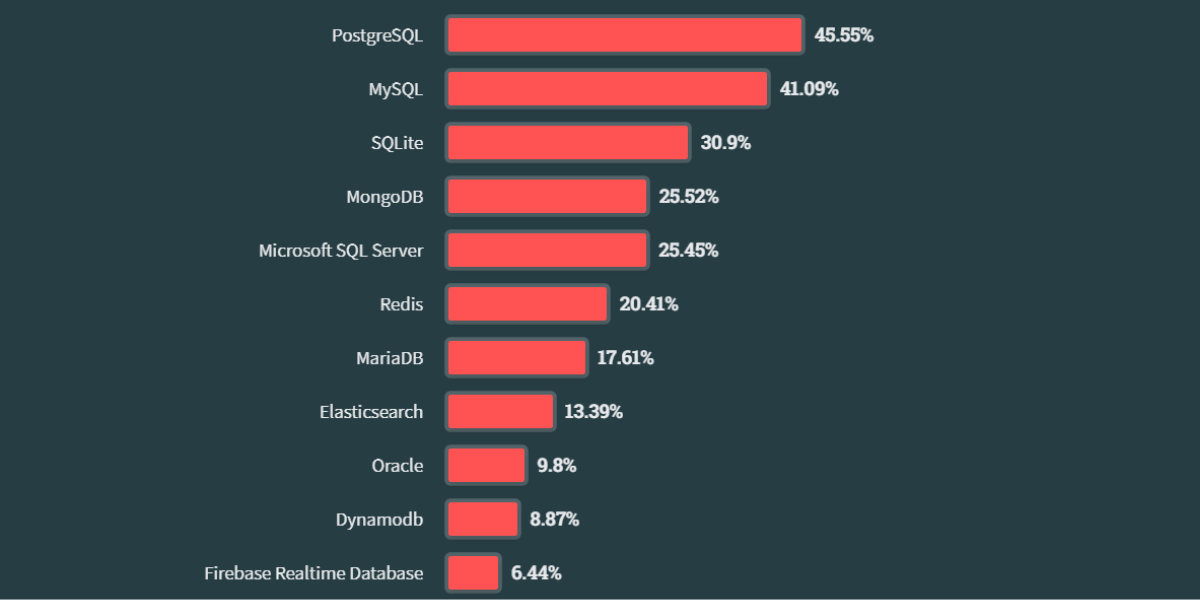
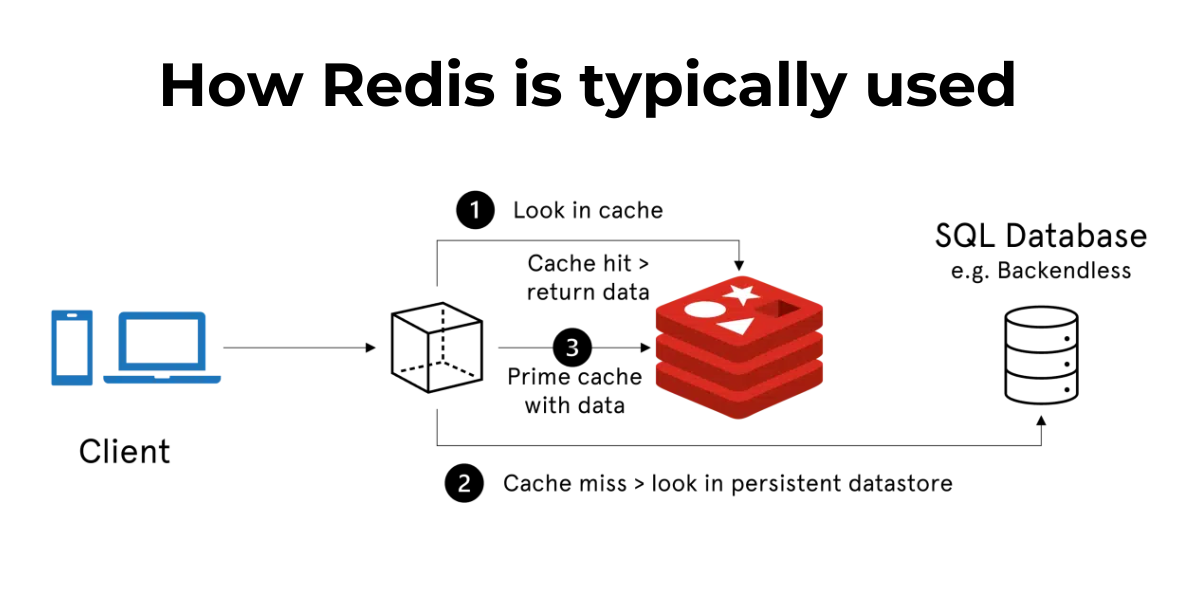
Redis is a fast and efficient NoSQL key-value database, ideal for applications requiring high performance. It stores data in key-value pairs, allowing for very fast data access. This list of features makes it a preferred choice for developers.
Its in-memory operation significantly contributes to its high performance.
Key-value databases like Redis are generally easy to use and allow for simple integration into applications. Their key-value operation enables very fast data access, which is crucial for applications requiring immediate response times.
Additionally, they are versatile and can be used for various applications, from user sessions to result caches.
However, one of the main challenges with Redis is the risk of data loss in case of failure. This risk is particularly relevant for applications that require high data availability.
While backup solutions exist, they require proactive management to ensure data security.
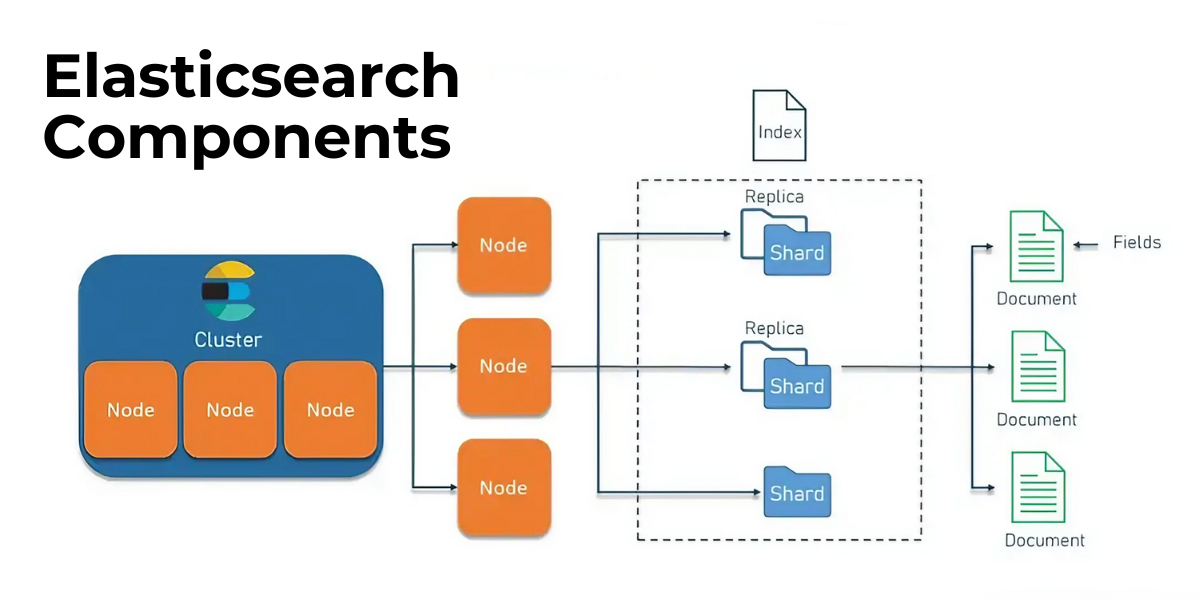
Elasticsearch is an open-source search and analytics engine based on Apache Lucene, designed to process large amounts of data while providing fast search results. Its ability to efficiently manage searches on massive data volumes through its document-oriented architecture makes it a powerful tool for businesses.
Elasticsearch allows for advanced full-text search, including features such as term and phrase matching. Its indexing engine eliminates stop words to optimize document search.
Additionally, Elasticsearch offers horizontal scalability, making it easy to add nodes to handle increased data or use cases. Plugins and security management further enhance the search experience.
Elasticsearch is deployed in log analysis to allow for quick visualization and extraction of critical information. It is effective for monitoring application performance, enabling log correlation to identify issues.
In the security field, Elasticsearch helps automate data correlation to detect network vulnerabilities.
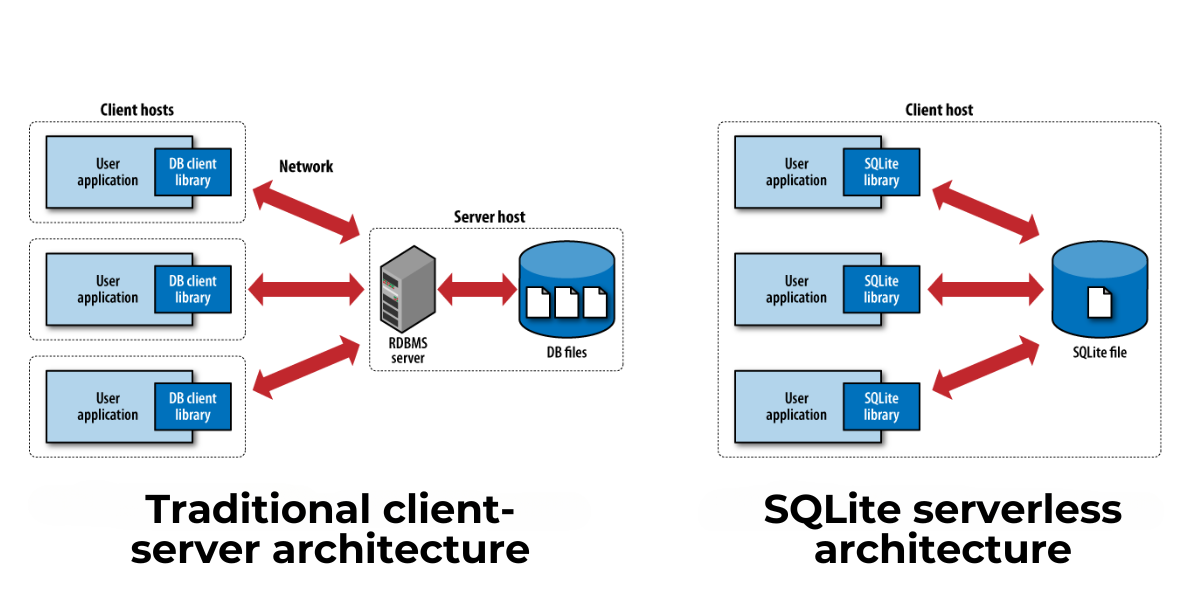
SQLite is designed to be integrated directly into applications, eliminating the need for a separate database server.
It can be used on various devices, such as:
However, SQLite does not support long-duration transactions, which can be a problem for applications requiring complex transaction management.
SQLite is extremely easy to set up and manage, making it an attractive option for developers. As a standalone database, SQLite is portable and can be easily integrated into various applications without external dependencies.
Additionally, SQLite operates without a server and without requiring prior configuration, allowing for immediate use upon installation.
However, SQLite may encounter limitations in its ability to manage very large databases. SQLite’s performance may significantly decrease when confronted with large-scale databases.
These limitations can complicate the management of complex transactions, leading to issues such as locking.
Cassandra is a distributed NoSQL database, designed to handle large amounts of data with high availability. It operates by distributing data across many interconnected servers, optimizing availability and fault tolerance.
Well-known companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix use Cassandra for its ability to handle vast amounts of data.
Cassandra is particularly effective for managing a large number of writes, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent data writes. Its architecture relies on peer-to-peer replication, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
Cassandra’s scalability allows for easy addition of nodes to the cluster without service interruption.
However, managing Cassandra can be complex, requiring advanced technical skills to configure and maintain a cluster.
Additionally, Cassandra can have high resource needs, which can lead to increased operational costs.

MariaDB is known for its improvements in performance and security compared to MySQL, making it a viable open-source alternative. Many organizations have migrated to MariaDB due to its advanced capabilities and improved performance.
MariaDB includes a multithreading feature that allows it to handle up to 200,000 simultaneous connections, surpassing MySQL in this area. It also features a storage engine called MyRocks, optimized for better performance with flash storage.
Additionally, MariaDB supports additional storage engines not available in MySQL, such as XtraDB and Aria, and offers advanced features like dynamic columns.
Many organizations, including the Wikimedia Foundation and Google, have migrated from MySQL to MariaDB to take advantage of its advanced capabilities and improved performance. These migrations reflect the trust placed in MariaDB in critical environments requiring increased reliability and performance.

| Database | Project Use Case | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | Applications requiring flexible data management | Flexibility and scalability | High memory consumption |
| PostgreSQL | Transactional applications with strict standards | Reliability and JSON support | Limited to transactional applications |
| Oracle Database | Enterprise solutions with high performance and security | Built-in security and high performance | High cost and complex implementation |
| MySQL | Web applications and open-source projects | Free and easy to use | Performance issues with large data volumes |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Advanced data management for enterprises | Easy integration with Azure | High cost and complexity |
| Redis | Applications requiring fast in-memory performance | High performance for in-memory data | Risk of data loss in case of failure |
| Elasticsearch | Applications with large amounts of data to analyze | Powerful search and analysis engine | Complex management and requires technical skills |
| SQLite | Embedded projects requiring a lightweight database | Easy to set up and use | Limited in managing large databases |
| Cassandra | Projects requiring horizontal scalability | Scalability and fault tolerance | Complex management and high resource costs |
| MariaDB | An alternative to MySQL for improved performance and security needs | Improvements in performance and security | Compatibility and support of some engines are limited |
In 2024, choosing the right database is a strategic lever for business performance and growth. MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MySQL, and many other solutions each offer unique strengths, whether it’s flexibility, scalability, or robust data management. MongoDB, for example, is attractive for its flexibility, while PostgreSQL stands out for its reliability and compliance with transactional standards.
However, it’s essential to consider criteria such as security, costs, or the ability to handle large amounts of data. Making the right choice will allow your company to optimize its information management and make informed decisions. Whatever your project, the ideal database exists to support your growth.
Databases are indispensable in 2024. They ensure quick access to crucial information for businesses, thereby fostering their growth and performance. They also facilitate the storage, management, and analysis of large volumes of data in response to the rise of Big Data.
MongoDB offers many advantages! Notably, exceptional flexibility thanks to an adaptable schema and the ability to perform complex analyses through its aggregation framework. This makes it easily adaptable to the evolving needs of applications.
PostgreSQL is favored for transactional applications due to its reliability, adherence to standards, and advanced features such as JSON format support. These characteristics make it an optimal choice for systems requiring rigorous transaction management.
Yes, Oracle Database can be expensive for small businesses due to its high pricing and implementation complexity, which often requires specific technical expertise.
MariaDB stands out from MySQL with its improved performance and security, as well as advanced features like multithreading and the MyRocks storage engine. These advantages encourage many organizations to adopt MariaDB.

ITTA is the leader in IT training and project management solutions and services in French-speaking Switzerland.
Our latest posts
Subscribe to the newsletter
Consult our confirmed trainings and sessions

Nous utilisons des cookies afin de vous garantir une expérience de navigation fluide, agréable et entièrement sécurisée sur notre site. Ces cookies nous permettent d’analyser et d’améliorer nos services en continu, afin de mieux répondre à vos attentes.
Monday to Friday
8:30 AM to 6:00 PM
Tel. 058 307 73 00
ITTA
Route des jeunes 35
1227 Carouge, Suisse
Monday to Friday, from 8:30 am to 06:00 pm.